
When you pay a visit to your local piercer and look at the tremendous variety of jewelry in their display case, it’s easy to assume it’s always been that way. What’s difficult to believe is that before Gauntlet, piercing enthusiasts were making do with earrings and all kinds of improvised contrivances. Although I’m always reluctant to blow my own horn, the truth is that I was personally responsible for many of the jewelry designs and piercing innovations most people take for granted.
Despite Doug’s financial help, my budget was still very lean. I had little knowledge of photography, especially taking pictures of jewelry, which is an art unto itself. Since I couldn’t afford to hire a professional photographer and printing photographs would have been more costly, I chose to illustrate the first brochure myself with line drawings. In these days of desktop publishing, younger people have no concept of what was involved to produce printed materials before the advent of the home computer. The process was in constant evolution, but in the mid 70s a common way was to take the copy to a local printer. There someone would type it into a special IBM Selectric typewriter — anyone remember typewriters? — equipped with memory. At the push of a button the text would then be printed onto special paper that would later be cut up and pasted by hand into the final layout. All very primitive by today’s standards. Headlines were often produced separately using fonts that were on a strip of film. Each letter was exposed onto light sensitive paper and when finished, processed in photo chemicals. As an alternative you could do as I did and use rubdown lettering for headlines. I was still groping my way. It took time to design and “test drive” the nearly dozen items that appeared in the first brochure. As mentioned in an earlier column, my first design was the nipple retainer. The bead ring, a scaled up version of a fairly common earring design, followed this. In the months and years to come, jewelry designs were always being developed and refined. Some became classics that are still being reproduced today; some were consigned almost immediately to history. Others lasted for a while, eventually fading into obscurity for lack of interest by customers. Still others ended up on the scrap heap because experience proved a particular design was no longer appropriate. Regardless of their longevity, many of them have an interesting story. For a great many years the standard bead ring with the attached ball was Gauntlet’s bread and butter. But some members of the T&P group, and others, wanted a design that appeared to be continuous. Had it been practical they would have been quite happy to have the rings permanently soldered shut. One of Gauntlet’s early competitors was a short-lived business called Whatever Rings. It was run by a couple of gay guys who were heavy S/M players. They operated out of their West Hollywood apartment and solicited business through ads in the local gay press. The business was primarily a means for them to entice men into an S/M scene. The “jewelry” sold by Whatever Rings consisted of gold wire formed into simple gold rings. There was no closure. While they might look nice, I personally considered them impractical if not dangerous. From experiments I had done I knew it was difficult to get the ends to line up perfectly, particularly after the ring had been inserted into a piercing. This could mean discomfort if the gap rotated inside the piercing. The gap, no matter how small, could also trap debris and quickly become a breeding ground for germs that could lead to infection in a fresh piercing.
 The “Seamless” Ring.
Unfortunately one of my customers discovered the shortcomings of the design not long after I’d inserted them into his nipple piercings. His name was Alden, and he was part of the T&P group. He also enjoyed rough sex play. Early one Monday morning he showed up on my doorstep. It was obvious something was wrong. Apparently he’d gotten into some pretty heavy action on Saturday night. Someone he was playing with got a little too rough with his nipple rings and one of them had sprung open inside the piercing. He couldn’t rotate the ring or remove it and was in great discomfort. I had to open the ring with a pair of ring expanding pliers in order to remove it. After that he understood the benefits of wearing a ring with a closure especially if he planned on a rough night.
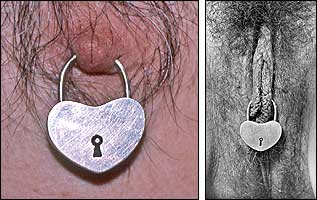 Handcrafted jewelry locks Back when I’d lived in Denver I’d wanted to put a lock in my ear piercing. In the early 70s it was uncommon for a man to have an ear piercing at all, and stretched piercings were something you only saw in National Geographic. There was no way I could see to get a lock through my ear. I had some basic jewelry making tools and was easily able to get some silver sheet and wire. Using these I constructed a crude working lock. This design with its broken shackle and another with a solid one, made their way into my first jewelry brochure. Unfortunately these handcrafted locks were never practical. If worn on any semi-permanent basis, they would soon become bound up with disgusting gunk and nearly impossible to open. I attempted unsuccessfully to remedy the situation by replacing the tiny spring with a pad of silicone rubber. Making the locks became a job I dreaded. They involved a lot of work that seemed wasted because of the inherent problems. By the time I issued my second brochure I’d dropped the design with the broken shackle replacing it with a simulated lock that needed no key and had no mechanism to get fowled up. Eventually I discontinued locks altogether.
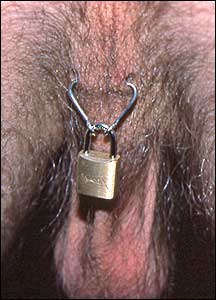 A jewelry prototype that never made it into production.
There were a few hardcore souls who seriously did want something permanent. Soldering, of course, was out of the question. I did find one successful solution. The balls on our standard bead ring were hollow. I would cut a groove around the end of the ring that went inside the ball and fill it with epoxy. When the ring was closed the cement would be forced into the groove where it would set and make the ring impossible to open.
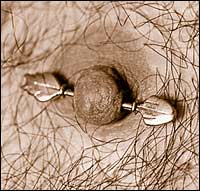 Arrow of Eros
 Some of the many barbell variations offered by Gauntlet. Over the years many other variations were introduced. None of them were ever as popular as the initial one with round balls which made it much more versatile.
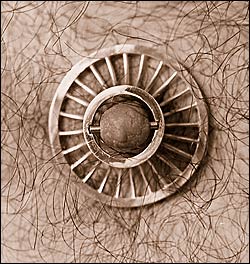 An early nipple shield design. At one point I contemplated using spring-loaded watchband pins to hold the shields on, but this proved impractical and unnecessary. The tension of the stretched nipple was sufficient to hold the shield in place. S/M also had an influence especially on one particular design. Even in the early days there were people into play piercing. For them I came up with something like a spoked wheel which had a little more depth. This drew the nipple out so that hypodermic needles could be inserted through the spokes.
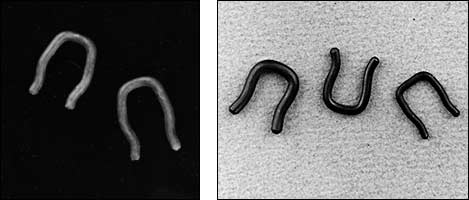 The septum retainer was a major breakthrough. (Left: the original septum retainer, right: niobium retainers)
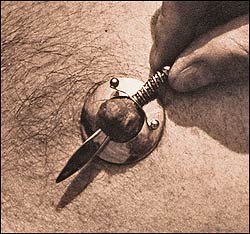 Custom nipple jewelry.

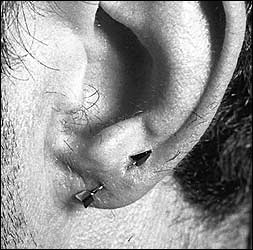
One of my more colorful clients was a Hungarian doctor who showed up on my doorstep one day. I was still working out of the house at the time, and he’d been referred to me by the Pleasure Chest, a sex shop that had recently opened in West Hollywood. Dr. C was impeccably dressed in a suit and tie and had the bearing of a European gentleman. He explained that he wanted a frenum piercing. This was accomplished without a great deal of fuss. I must confess I was a bit more nervous that usual. Although clean, the house and furniture were shabby. He was, after all, a doctor, and I was concerned that he would be uncomfortable being pierced in such an environment. Still, I brought out a clean bath towel and spread it on the couch for him to lie on. I laid out the bagged and sterilized equipment on a stainless tray. When I was finished he complemented me my technique as well as the cleanliness that I observed. It was a particular validation coming from him.
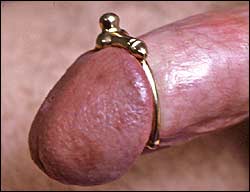
Dr. C was quite happy with the finished piece of jewelry. Unfortunately he didn’t feel comfortable wearing it all the time, especially at the health club. Consequently he took it on and off frequently. Eventually the post would break off, and he would bring it to me for repair. The last time this happened he brought it in and chatted amiably about what a wonderful device it was. I told him how long it would take for the repair, and everything seemed satisfactory. I never saw him again. Whatever happened to him I never found out. After holding onto the piece of jewelry for several years, I eventually sold it.
Gauntlet’s transition to stainless production was not an easy one. I resisted as long as possible and finally gave in because the price of gold had begun to rise alarmingly. The challenges were many. First and foremost it was necessary to determine which of the hundreds of stainless steel alloys was appropriate for inserting into the body. The best information I was able to gather was that it needed to be low-carbon and nickel-free. At various times we made jewelry of 304 and 316 stainless. The industry standard today is 316L. Then there was the matter of gauge. The standard gauge system used for steel wire is different from that used for gold and silver, so for the sake of consistency it was necessary to have all the stainless steel wire custom produced. The coils of wire arrived from the mill and I discovered that it was too stiff to be easily shaped. Gold and silver can be softened, a process called annealing, quite easily by heating them red hot and quenching them immediately in cold water. If you do this to steel you only make it harder. The only way to get the wire soft was to send it out and have it professionally heat-treated. At first I tried unsuccessfully to apply gold fabrication techniques to stainless steel. The results were disappointing to say the least. Eventually I found a company that was able to silver solder drilled stainless balls onto stainless steel rings and then electropolish them. For some reason the quality of the electropolishing was not reliable. Sometimes the surface was not mirror bright and on occasion the process was overdone and the rings came back measurably thinner than they should have been. Many of these problems could have been eliminated had I not been convinced that the captive bead ring design was unsatisfactory. As someone who continually thought of piercing as an adjunct to sex play, I felt the ball could too easily come loose and get lost. I couldn’t imagine many people wanting to search for a ball lost inside a body cavity. Stainless steel barbells presented their own difficulties. There was no way to produce them in house, so I went looking for a machinist to do the job for us. Part of the problem was that I had no idea how to locate the right person. The results were less than satisfactory. The first order of barbells I had made should never have seen the light of day much less been offered for sale. The machinist was unequipped to produce a stud with an internally threaded post. I ended up settling for externally threaded studs, and to say that I was frustrated is putting it mildly. In order to insert them without causing discomfort or damage to the individual, the externally threaded post first had to be dipped in melted wax. It was a compromise I hated. When the stock began running low I started looking for another machinist and finally found one who was able to produce an internally threaded barbell stud. Unfortunately that was only half the challenge. The other was to produce a ball with male thread attached. The machinist produced short threaded pins that had to be secured into drilled and threaded balls. We tried various kinds of cement without success and ended up having to silver solder them. It was a solution, although again less than 100% satisfactory. On occasion clients would ask why Gauntlet’s stainless steel jewelry was so expensive. I always told them that they could buy a nut and bolt at the hardware store for pennies because they were manufactured by the millions. At that time there simply weren’t enough people who needed stainless steel body jewelry to mass produce it like hardware. All that has certainly changed.

The anodizing process required that the metal piece be attached to an electrode and submerged in a solution mostly of water. The more oxygen the solution could make available to the process, the better the results. Different craftspeople had their own secret formulas. I heard of someone who used Coca-Cola. What seemed to work best for me was a solution containing non-chlorine bleach. Since there is no practical way to solder niobium, I finally was forced to embrace the captive bead ring. From then on it became part of Gauntlet’s jewelry line. It’s been almost thirty years since I started Gauntlet, but the ideas and innovations that it pioneered are very much with us today. I often wish I were receiving royalties. I’d be a very rich man.
IAM members click here to discuss this article.
 Jim Ward is is one of the cofounders of body piercing as a public phenomena in his role both as owner of the original piercing studio Gauntlet and the original body modification magazine PFIQ, both long before BME staff had even entered highschool. He currently works as a designer in Calfornia where he lives with his partner.
Copyright © 2004 BMEZINE.COM. Requests to publish full, edited, or shortened versions must be confirmed in writing. For bibliographical purposes this article was first published May 28th, 2004 by BMEZINE.COM in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. | ||||||||||||||||







