|
||||||||||||||||||
Suspensions & Tensions: Yesterday
|
||||||||||||||||||
"Your body belongs to you, and in the appropriate ritual, it has been given to you to explore the full dimensions of your being."
In 1943, a young teenage boy in South Dakota was bored to tears in the stifling, restricted and limited environment around him. He haunted libraries hoping to find a glimmer of something different, exciting, vital and alive in the world beyond. In the school library, in a musty alcove he hit pay dirt — a complete collection of old National Geographic magazines dating from 1905! Here were pictures of people who looked different, lived differently and had done radically different things with their bodies. This was exciting, WOW!
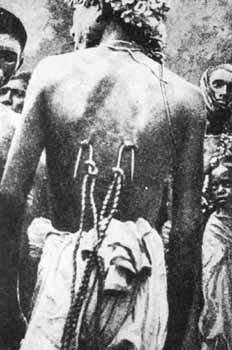
Discovery of these Native American rituals rang many bells for the boy since many of these rituals had taken place in the same physical space in South Dakota he now occupied, and only about fifty years prior. Following a psychic trail on his bicycle, he found several places where Lakota, Arikira and Sissiton peoples had pierced their flesh and pulled against it. The vibes were still there beneath the rustle of cottonwood leaves on the trees from which they pulled and hung. The feeling left in these places was infectious. The boy was intoxicated by it. He had to try this himself. In fact, he felt like he had done this before. That boy was me. He has since tried these body rituals many times. Now some fifty years later, in 2003, he finds himself in a strange new world — one where many others have also felt the urge to pierce their flesh and either pull against it or be suspended by it. However, some of these explorers seem to think they’ve just invented the wheel and want some kind of patent on it to claim ownership. So now we’ve got “Superman” and “Coma” suspensions and other new names that just didn’t exist in the world of the people who originated these rituals. But that is ok as long as some credit and honor is paid to the people who came before and showed the way — as long as the inner “magic” and “sacred space” belonging to these rituals is not forgotten or ignored. ORIGINS & BELIEFS The practice of piercing the flesh then pulling or hanging by pierced body parts is not a new custom. It has been a part of Hindu Culture in Southern India (Tamil Nadu) for thousands of years, nearly as long among the Sufi of the Middle East, and for hundreds of years as a part of religious ceremonies of Native Americans. It is, until recently, an alien and forbidden custom in mainstream Western Cultures. What useful purpose could this custom have? Why would anybody deliberately choose to “mutilate” their flesh and “suffer” thus? A huge conflict exists between Western Culture and those where such piercing rites are honored and encouraged. The core of this conflict centers around different cultural beliefs about the body. Who does your body belong to? A distant God who has strict rules about what you can do with it? Or to a Priest or other intermediary of this real or imaginary divinity? Does your body belong to a father or mother? Or to a husband or spouse? Or to the state or a social order or tribe? Does anyone besides you have the right to decide what you can or cannot do with your body? Or does it simply belong to you the one who lives inside? In those cultures where piercing ceremonies have developed, the attitude is pretty much universal: your body belongs to you, and in the appropriate ritual, it has been given to you to explore the full dimensions of your being. In Western Cultures of the late 20th Century, some of these alien beliefs have replaced old Judeo-Christian ones. Since the 1970’s the widespread practice, acceptance and popularity of body modification definitely says, “My body belongs to me!” However, like many customs and practices that originated in other cultures and were transplanted here, only part of the messsage seems to have been transmitted. For example, the art of tattooing was brought to Europe from the South Pacific by sailors and early explorers. In Somoa and the Marquesas, the custom of tattooing was a very sacred and special rite: “the making of a magic mark”. It was an initiation, a rite of passage, and meant to transform forever the one who bore it. The early sailors brought back the technique to make the mark — but failed to bring back the magic. So soon European tattooing became a mere novelty: marks that don’t wash off, a status symbol of sailors and outcasts. The meaningful and magical geometric designs of the originators were replaced with the only kind of graphic Europeans understood: crude representational pictures or words. The magic and purpose of the originators had been lost in translation. In most cases, I feel the same thing has happened to the suspensions and related piercing experiences a lot of people are doing today. They are often being done for sheer novelty, attention, and ego satisfaction. I feel very strongly that if one borrows a custom from another culture, it is your obligation to respect and understand, as best possible, the significance and mystery of the practice. Otherwise, it can easily fall into darkness or misuse and undesirable consequences or spiritual degradation can result. However, at the same time, I feel everybody has a right to do what they will with their body even if it is for sheer exhibitionism. But they should be aware they are missing the full potential and magical significance of the act. SAVITE HINDU & SUFI PRACTICES The oldest recorded history of piercing the body and pulling on or hanging by the piercings goes back perhaps five thousand years to the earliest cultures of India. In this great period of human development in the East, the concepts of Hinduism including the various yogic disciplines, understanding of energy centers (chakras), tantra and the Kama Sutra were born. The body/spirit connection was especially explored, and the ability to attain different states of consciousness was both sought after and revered. The idea of “using the body to transcend body” played an important role in religious and everyday life. Two major Hindu Festivals are especially focused on body piercing rituals: Thaipusam in January/February and Chidi Mari in May/June. Both festivals are celebrated primarily by Savite Hindus (devotees of Lord Siva, Muruga, Murugan, Subramanya, the Great Mother Mari and Kali). Other Hindus, like the followers of Vishnu or Krishna, do not usually practice body rituals or employ body piercing in their religious practice. In fact, they often hold these rites in contempt. The Savites are mostly the dark-skinned Tamil people of Southern India (Tamil Nadu) and direct descendents of the original indigenous peoples of India. Their Tamil language used in the chants of their “Pujas” (worship) is the spoken equivalent of the ancient written language of Sanskrit. Historically, the Tamil peoples have been persecuted for hundreds of years. First by the light-skinned Northern Indians, descendents of Aryan invaders, then by the British colonialists who hauled them off as virtual slaves to work on tea plantations in Ceylon (now Sri Lanka) and other parts of the British Empire. Wherever they’ve been taken by force, the Tamil people have been remarkably successful in preserving their culture and spiritual practices. Something similar is now happening with the culture of Tibet.
Thaipusam is a piercing festival to Lord Siva and especially the Hindu dieties who are “Stars in His Crown”: Muruga, Murugan, Subramanya, Skanda, Ganapati. Devotees vow to bear a gift to the deity (archtype) under physical hardship. This is considered the purest of gifts — the offering of one’s own body pierced with spears, skewers or hooks as it delivers the gift. This is “Worship Through the Body” and such a gift is especially accepted and blessed by such deities (archetypes) as Murugan, Lord of Piercing and patron Saint of the Tamils. When I witnessed the Thaipusam in Penang Malaysia in 1995, I felt the reality of the sacrificial energy released. It was overpowering, intoxicating, sweet, and very similar to the energy that I have experienced at many of the body suspension and hook pulling rituals I have facilitated or witnessed in recent years. This same energy has historically been a part of Sufi body piercing rituals dating back hundreds of years. In case you don’t know, Sufi is a fusion of ancient Hebrew, Hindu, and Islamic beliefs and practices with emphasis on individual “gnosis”, that is “direct knowing” by means of altered states. Sufi sects that still practice piercing rituals, dervish dancing, and other trance rites are not accepted by mainstream Islam and have been forced underground except in the United States and a few other Western cultures. I even know of one of them in Marin County, California! One of my ardent pro body piercers learned Arabic and was attached to that group. My namesake, the original Fakir Musafar, was a 12th Century Sufi mystic from Meshed, Persia (Iran) who for sixteen years had six daggers embedded in his chest and back plus six horseshoes suspended from twelve permanent piercings in his shoulders and arms. Musafar’s message was much the same as mine: one can access the unseen worlds and find the source of being through the body. Legend has it Musafar was ridiculed for his bizarre practices and that he died of a broken heart because his message went unheard. In many ways, I feel the hand of Musafar and the energy of Murugan in what I have been doing for some fifty years. I also feel the Spirit of the Modern Primitive is an extension of that same ancient and timeless energy. NATIVE AMERICAN PRACTICES
After many days of fasting and extreme ordeals, Mandan young men who were about to become adults and enter adult life were pierced twice in the chest and twice in the back. Under the guidance of an older man who had taken this journey before, often many times (called a Ka-See-Ka meaning guide), they were suspended by either set of piercings from the roof of a lodge. In extreme pain, followed by trance, the young men were hung up for about twenty minutes to seek communion with “The Great White Spirit”. Legend has it that initiates traveled out of their bodies in this state and were guided through unseen worlds by their Ka-See-Ka who knew the way. The O-Kee-Pa journey was like a canoe trip on a tricky river: the initiate submitted and just rode in the canoe while the Ka-See-Ka steered it to appropriate vistas and to avoid rocks. Through the years, neighboring tribes, especially the Arikara and Minnetaree, were exposed to the Mandan ritual and developed their own piercing rites, often more severe. Various Sioux (generic French word used for all tribal peoples living in this area) tribes like the Lakota, Ogalala, Teton and Yellow Hand also adopted or developed shamanic piercing rites — chief of which is called the Sun Dance in which pledgers are pierced once or twice in the chest, fastened to a tree or pole and vow to pull against the piercings until the flesh breaks. Again, the object is to enter an extraordinary state and meet an animal ally or the “Great White Spirit” — either as communion, healing or to obtain special knowledge. The most serious initiates and experienced dancers gained great respect and awe for how long they could pull against the piercings without breaking free. Sometimes this would be several days. Wonderfully accurate movie reenactments of the O-Kee-Pa and Sun Dance can be seen in the Richard Harris films “Man Called Horse” and “Return of the Man Called Horse”. A documentary film of a real modern day Sun Dance and O-Kee-Pa style suspension can be seen in the film “Dances Sacred & Profane” shot in Wyoming with Jim Ward and Fakir as initiates. When this film was released on videotape it was called “Bizarre Rituals”. Watch my web site for a new tape to be released soon with the last thirty minutes of the “Dances” film plus a short profile of Fakir produced by French filmmakers and Canal+ for European distribution. Yours for safe and enlightened body rites,
In my next column, SUPENSIONS & TENSIONS: TODAY, I will bring these practices to contemporary times with accounts of my own experiences and the experiences of others. I also wish to alert those who currently do piercing rituals with large hooks of a new and recent danger: MRSA (Methicillin Resistant Staphylcoccus Aureus), a staph infection that is resistant to all current forms of antibiotics. It is real. It is here and I recently had to deal with a case that required two open-heart surgeries! It is easily transmitted by mere physical contact. It is then called CA (community acquire) MRSA. More on this new danger in my next column.

Fakir Musafar is the undisputed father of the Modern Primitives movement and through his work over the past 50 years with PFIQ, Gauntlet, Body Play, and more, he has been one of the key figures in bringing body modification out of the closet in an enlightened and aware fashion. For much more information on Fakir and the subjects discussed in this column, be sure to check out his website at www.bodyplay.com. While you're there you should consider whipping out your PayPal account and getting yourself a signed copy of his amazing book, SPIRIT AND FLESH (now).
Copyright © 2003 BMEZINE.COM. Requests to republish must be confirmed in writing. For bibliographical purposes this article was first published November 15th, 2003 by BMEZINE.COM in Tweed, Ontario, Canada. View all columns by Fakir Musafar | Return to BME/News | ||||||||||||||||||