|
Fighting For Freedom In Iraq One Screaming Eagle At A Time
I have hope for any culture that allows a tattoo studio to exist. Any culture that permits its people to choose their own tattoos has made a very important statement that is all too rare in this world: the citizens, not the government, own their bodies and have full sovereignty to decide what will become of them. This is the most base and important right that a person could have — and one that people in the US state of Oklahoma still don’t enjoy… unlike Iraqis.
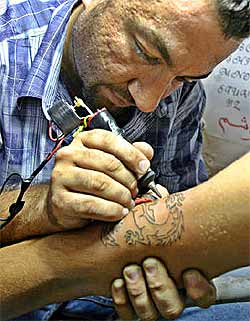
It is true that tribal tattooing has been popular in Iraq for thousands of years — even Saddam Hussein had protective glyphs tattooed on him, and in her book NPR correspondent Anne Garrels describes seeing heavily tattooed Shiite mothers in the overflowing hospitals created by the wars. In addition, after the first Gulf War left so many Iraqis without hands, arms, feet, and legs, Sharia courts which often amputate these parts as punishment started to add tattoos to the foreheads of criminals so that war amputees wouldn’t face the stigma of people assuming they were criminals. But all of this tattooing is very different than what happens in a Western-style tattoo studio. Until recently, all tattooing in Iraq was legally limited to permanent marking designed to uphold social order — that is, the tattoos were for communities, not for individuals. Similarly, Oklahoma permits cosmetic tattooing — that is, tattooing which allies an individual to the group aesthetic. Reuters is currently reporting on Sarmad Shamael, a quiet 29-year old who has a small basement tattoo studio in one of Baghdad’s many rough neighborhoods. Instead of using breast milk and ashes to scratch traditional designs, he uses architect’s ink and a homemade tattoo machine to render the same sorts of images you might see anywhere in America — “Celtic crosses, screaming eagles, and death’s heads” as well as plenty of dragons from a beat-up book of tattoo flash he managed to import.
 Sarmad Shamael at work in his tattoo studio Photo: REUTERS/Ceerwan Aziz The new Iraqi government is certainly no more liberal than Saddam was, but thanks to an almost total collapse of government since the occupation started, Iraqis are operating in a lawless environment — it’s not so much that tattooing has been made legal, it’s more that there’s no one enforcing the laws. As Sarmad puts it, “now people have a choice about what they do, there are no laws to restrict them.” This is true across Iraq as formerly banned industries and subcultures ranging from pornography to heavy metal to pharmacological vices flourish. The mainstream of Iraq — like the mainstream in the West — likes to call them “the bad side of freedom” and debate whether it’s an American conspiracy to corrupt their culture. At first after Saddam’s fall, Iraqi police continued to enact the vice laws, but American MPs, seeing overflowing prisons, forced the Iraqis to release people who committed these crimes and the official raids stopped. The main risk comes from religious vigilantes who have been bombing businesses that they don’t agree with. Al Khayam theatre, near Sarmad’s tattoo studio, has recently began showing adult movies — “In Saddam’s time I had one old night watchman. Now I have three young people armed with Kalashnikovs,” said the manager. Sarmad’s customers as well face resistance to their tattoos, with one 19 year old — tattooed with a scorpion and an American Indian head — describing his father trying to burn his tattoos off with acid. Luckily his mother convinced his father that “the damage was already done,” and now young Mohammed Jasim, presumably having saved up another $15, is back in the rusty metal tattoo chair.
Business is still slow, with Sarmad doing a tattoo only every few days since he opened last April, but he’s improving, and doing his best to control contamination inside his studio. He doesn’t advertise, promoting himself only by word of mouth and the large lion and dragon he’s tattooed on his own forearm underneath the text, in English, “I want to kiss you.” Salman Rushdie recently argued that the level of freedom in a culture can be gauged by its willingness to accept pornography. “Pornography exists everywhere,” he wrote. “But when it comes into societies in which it’s difficult for young men and women to get together and do what young men and women often like doing, it satisfies a more general need. While doing so, it sometimes becomes a kind of standard-bearer for freedom, even civilization.” While I certainly agree with Rushdie, I think at an even more base level, it is tattooing of the individual that is the best indicator of how free a culture is. A culture that tolerates people tattooing themselves as they see fit — not as the law, the tribe (or even the family), or their social stature dictates — is a culture that tolerates the idea that people own themselves. The belief in self ownership, rather than ownership by the tribe, is the first and most important step toward true personal liberty and all that comes with it. Pornography is the second stage of freedom, as it enacts the right to use one’s body as a form of communication with others in any way one sees fit. But both of these freedoms boil down to the same thing — being allowed to do whatever you want, no matter how odd it may seem to others, as long as you’re not hurting anyone else. “A lot of people ask me, why are you so strange,” says Sarmad Shamael, sitting in his little tattoo studio in Baghdad. “I tell them: because I like it.” |
Post navigation
 BME/News and Modblog highlight only a small fraction of what BME has to offer. Take our free tour and subscribe to BME for access to over 3 million body modification related photos, videos, and stories.
BME/News and Modblog highlight only a small fraction of what BME has to offer. Take our free tour and subscribe to BME for access to over 3 million body modification related photos, videos, and stories.