(Author’s note: Excuse me while I get all meta on you.)
Full-disclosure time: When I first saw on Lane Jensen’s IAM page pictures of the microdermal he’d put into someone’s eyelid, I was mortified. This was too much, too risky, and, though I had not been apprised of the details of the situation, it read as irresponsible at best and fame-seeking at … well, not quite “worst,” but getting there.
The client, it seemed, was quite young [Author’s note: She was 17 years old and her father was present. My point stands, nonetheless], with minimal visible prior body modification work done — not to say she was too immature, but, in the same way that most responsible tattoo artists will refuse to work on a lightly tattooed client’s hands or face, so should it be when it comes to highly experimental piercings (a distinction which, for the sake of this article, we’ll say includes microdermals). Because, as widespread as microdermals have become (and my God have they become widespread), this is still a new concept. The first images of microdermals (then called “dermal anchors” — oh, memories!) appeared on BME in an image update dated October 27, 2005. The first mention of them on ModBlog was April 15, 2006. On November 6, 2006, an article was published featuring interviews with a number of practitioners who had been performing microdermal procedures.
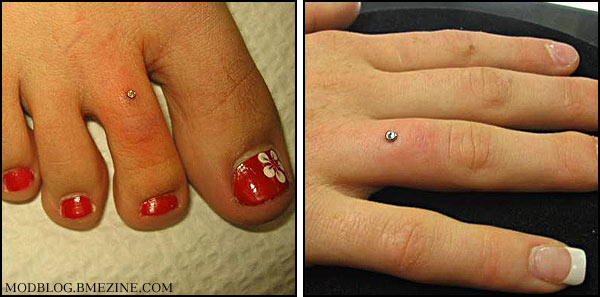 |
| ModBlog’s first microdermals |
So let’s say that microdermals are, in their current iteration (as a modernized and ostensibly simplified version of traditional transdermals), at most, about two-and-a-half years old. In most circles, this would place a project in its infancy — far from having been extensively tested or fine-tuned, and potentially rife with unknown (and sometimes well known) risks. (Very seldom are feature films released, for example, that comprise a series of unedited first takes.) Yet, in the body modification community, infamous for its impetuousness, two-and-a-half years is an eternity. The idea of the “guinea pig” is now largely irrelevant; as soon as something “new” has been done, provided the client doesn’t die on the spot, it’s added to the portfolio, uploaded to all manner of Internet forums and, if it’s interesting enough, it’ll probably even get posted on ModBlog.
Pardon me while I put on my ombudsman hat, but make no mistake: ModBlog takes a lot of blame here, playing the dual role of collective consciousness and enabler. Almost everything posted on ModBlog comes via BME submissions, which are filtered for funny, attractive and generally unique content, given a punny caption and then offered up to be criticized and lauded, copied and adopted.
That is to say, ModBlog is supposed to feature the best that BME has to offer.
Such is our position: We want to promote an environment in which new, exciting and beautiful procedures can be put on display and discussed, yet we’re also an archive, for whom comprehensive documentation is a mandate. Appearing on ModBlog, vitriol of the commentariat notwithstanding, is often a validation of sorts: If it’s good enough for BME to showcase, shouldn’t it be good enough for you?
Well, no. Not always. Sometimes in documenting things, we come off a little too enthusiastic about items that aren’t quite ready for prime time, or that we’ve convinced ourselves are worthy of attention simply because we’ve given them a lot of attention — the state of “being famous for being famous.” (See also: Anything related to Kim Kardashian or Brooke Hogan; Gawker’s tireless efforts to track Julia Allison’s every move; The Hills in its entirety.) Is this really a healthy phenomenon? Making stars out of people because of their physical modifications and creating an environment in which this miniscule level of fame can be achieved by pushing one’s limits further, harder and, quite possibly, dangerously quickly? There’s a fine line between celebrating the community and unduly, unfairly celebritizing its members.
And, like I said, this is, to an extent, our fault — “us” being the body modification media, slight as we may be. There is — be it real or imagined — an element of pressure to be more “extreme,” for lack of a better word (and there are many). On another forum, one commenter recently posted that he’d just passed his one year anniversary of entering the wonderful world of body modification, and posted the following laundry list of work he’d done (consider the entire quote [sic]):
septumx2, smileyx2,tongueweb, Apadravya, lorumx5, fingerwebx3, handwebx3, nipplex2, navelx3, lobex9, conchx2, helix/2g Dermal Punch, tragusx2, eyebrowx6, labretx10, “rhino”/unidentified
Though I definately don’t still have all those and I counted where I re-did piercings, I remember wach one… I wonder what mods are to come in the future?
Fifty-three piercings and six tattoos in one year. His first year. Holy crap. Another poster followed up with their own first-year anniversary inventory ([sic] again):
it all started with a septum piercing … It’s now at 1g … 0g flat punch, 0g conch punch, x4 vertical bridges, x4 horizontal eyebrows, 6 tattoos, 1 chest scarification, 6 lip piercings, venoms (now stretched to 10g), tongue webbing, ears pierced at 8g (now 5/8ths), multiple arm surface, belly button, clavicle surface, x2 nape, x5 lower back surface, tragus, smiley.
AND MANY MORE TO COME.
This isn’t a journey — it’s an obsession, whether it’s instigated internally, by a desire to fit in, lead the pack, or otherwise. A bodybuilder doesn’t start out deadlifting 700-pound weights. A mountain climber doesn’t scale K2 as an introductory ascent. This is unhealthy behavior, regardless of the outlet, but body modification allows for it rather easily — even encourages it, be it to pad a portfolio or to get one’s 15 minutes of ModBlog fame. If I had a nickel for every conversation I’ve had with people who mention the role that ModBlog played in the popularization of microdermals, well, I’d probably be able to afford to have one put in my eyelid.
This isn’t to decry experimentation or having fun with one’s body — Rachel posted a video of Lassi doing a guiche suspension a few weeks ago, for God’s sake. But this eyelid microdermal business is different; these images presented an ethical dilemma. By all accounts, it was awfully unsafe and, while not in direct contact with the eyeball, would potentially be a nightmare for the general eye-region. It’s one thing for a trained professional and experienced body modification enthusiast to throw a hook through his taint, but it’s another matter entirely to risk massive harm to a young, inexperienced client just because the opportunity presented itself and it seemed like an interesting procedure to try. I’m not an expert of anatomy, but one thing I’ve picked up on is that unless you are incredibly certain of your methods and the anticipated outcome, you don’t screw around with someone’s eyes. In a field in which calculated risk-taking comprises a significant portion of the action, simple consent should not be the be-all end-all for a practitioner when deciding whether or not to perform an experimental procedure.
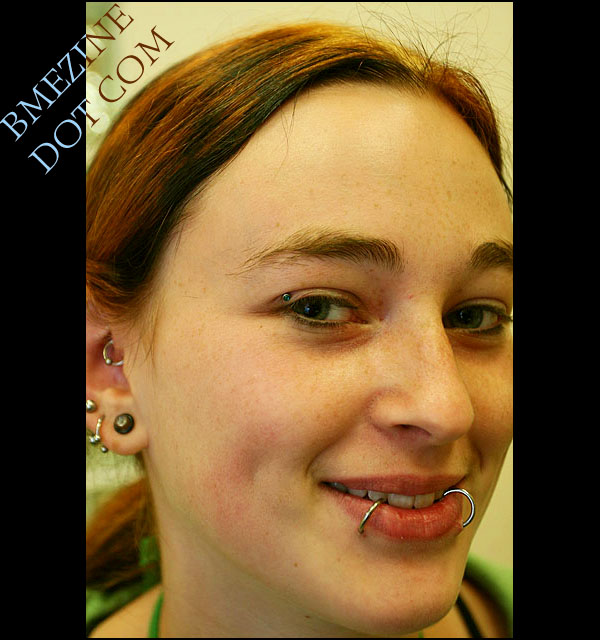 |
| The microdermal in question |
On the other hand, though? This was ModBlog fodder in every conceivable way. It was probably the first time it had been done, it looked healthy enough and, most importantly, it was new. Considering our standards, it probably deserved to be posted.
We decided not to post it. ModBlog’s influence is tangible, and we decided that appearing to endorse it in any way would have been irresponsible. Let’s wait, we thought, and maybe once we can see some results, we can determine if this is appropriate to post. It would end up in the BME image archives, of course, but ModBlog, to be sure, is a different beast altogether. This was a test — one that didn’t need to be publicized, and arguably performed on the wrong client. We didn’t want to be nannies or censors — BME would still accept the photos for its galleries — but as for ModBlog? This didn’t yet embody the best that BME had to offer. Body modification practitioners should cherish their guinea pigs — not exploit them.
Of course, being an online company has its drawbacks. Through a miscommunication, it ended up getting published on ModBlog. Naturally, some people loved it, some peopled hated it. Some claimed it was yet another moment in BME’s perpetual decline, while others probably asked their piercers if they could get their own (or, conversely, some piercers likely asked their clients if they were interested in trying it out). This isn’t a criticism of the chain of events: It’s just occurred enough by this point that there exists a recognizable pattern and, for the most part, we love it (see also: mustaches tattooed on fingers, etc.) — that’s why we do this. Body modification is a passion, and dealing with it professionally every day would be impossible if we weren’t legitimately excited by people’s experimentation and determination to modify and beautify themselves.
But that’s not an absolute, and it doesn’t mean that everything must be supported or looked upon favorably. Just because something can be done doesn’t mean it should be; there may be no right reasons for modifying yourself, but there are sure as hell wrong ones, and those are made substantially worse when the client is being used — whether it’s by the one performing the procedure or the one publicizing it.
(Ed. note: While Jordan is an editor for and a valued member of BME, this is an editorial and does not necessarily reflect the views of other BME staff or BME as a publication. As well, Lane has been invited to do an interview and defend his position. This will be published as soon as possible.)